Table of Contents
4 roller plate rolling machine is a widely used equipment for metal plate bending roll processing. It can realize the pre-bending and forming rolling of the plate, especially suitable for medium and thick plates and high-precision rolling processing.
Compared with the three-roller plate rolling machine, the four-roller plate rolling machine has the advantages of high degree of automation, simple operation and small residual straight edge.
1. What is a 4 roller plate rolling machine?
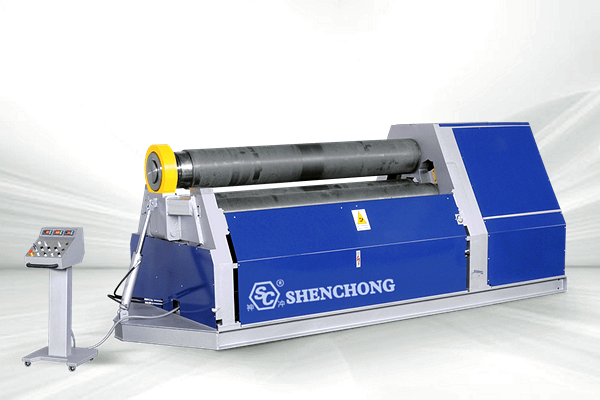

Definition:
A four-roll plate bending machine is a device that clamps, pre-bends and rolls the plate through the coordinated movement of four rollers (1 upper roller, 1 lower roller, and 2 side rollers). It can complete the symmetrical pre-bending and full-circle rolling of the plate at one time.
A 4-roll plate rolling machine is a mechanical equipment used to roll metal plates into cylindrical, arc-shaped or other shapes. It is widely used in pressure vessels, wind power, shipbuilding, petrochemicals, boiler manufacturing and other industries.
Brief description of working principle:
- Clamping the plate: The upper roller and the lower roller clamp the plate.
- Pre-bending: By lifting the side roller on one side, one end of the plate is pressed upward to achieve pre-bending (reducing straight edges).
- Rolling: The rollers move in coordination, and the plate undergoes continuous plastic deformation under the support of three points, and finally rolls into the required curvature.
- Discharging: The formed workpiece is unloaded through an auxiliary device or an upper roller flipping mechanism.
2. Structural composition of four-roll plate rolling machine
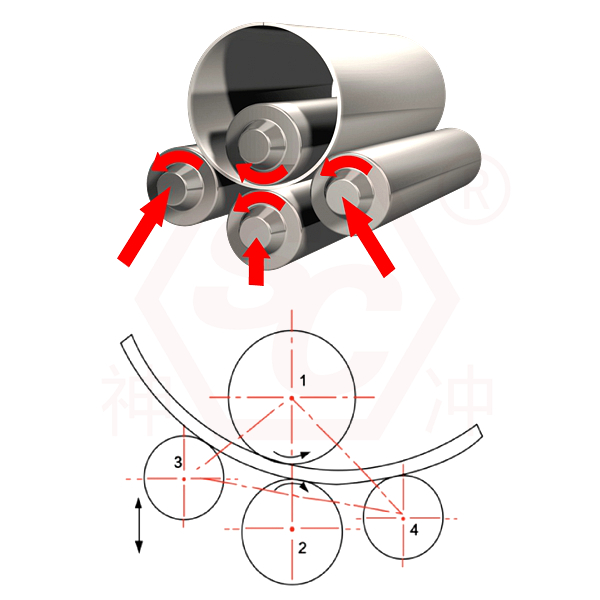
The basic structure of the 4 roller plate rolling machine is the basis for its automatic pre-bending, rolling and rounding functions. Compared with the three-roll plate rolling machine, the four-roll plate bending machine has an additional auxiliary roller (the second side roller), which greatly improves the processing efficiency and rolling accuracy. The following is the main structural components and functional description of the four-roll rolling machine.
1) Upper roller (upper working roller)
Position:
located at the top of the center of the frame.
Function:
The active roller drives the plate to rotate through the drive system.
Applies the main downward bending force to the plate.
Features:
Usually electrically driven, with the largest diameter, and can be lifted and lowered vertically appropriately.
2) Lower roller (lower working roller)
Position:
Located at the bottom, parallel to the upper roller.
Function:
As a driven roller, it plays the role of clamping the plate.
Can move up and down to adjust the clamping force.
Features:
Sometimes it is also a driving roller. Used to clamp and adjust the initial position of the plate with the upper roller.
3) Left and right rollers (side rollers)
Position:
On both sides of the upper and lower rollers, close to the lower roller.
Function:
Realize the pre-bending function.
Control the bending trajectory and forming radius of the plate.
Features:
Can be lifted or swung individually, usually controlled by a hydraulic system.
Their motion trajectory can be programmably controlled to achieve rolling of different shapes (cylinders, cones, etc.).
4) Main drive device
- Usually a motor + reducer.
- Directly drives the upper roller (or upper and lower rollers) to rotate and move the plate.
- Ensures a constant linear speed between the rollers to improve rolling accuracy.
5) Hydraulic system
- Controls the lifting and lateral movement of the lower roller and side rollers.
- Provides pressure control during rolling.
- Usually includes hydraulic cylinders, hydraulic pumps, control valve groups, oil tanks, etc.
6) Machine frame
- Supports the entire equipment structure.
- Ensures roller position accuracy and overall equipment rigidity.
- Made of heavy welded steel structures or castings to ensure strong load resistance.
7) CNC control system
- Used to operate the movement of various parts of the plate rolling machine and set parameters.
- Usually equipped with PLC, touch screen, human-machine interface (HMI).
- Realizes automated control and supports multi-segment rolling operations.
8) Auxiliary device (optional)
- Feeding device: such as hydraulic loading platform.
- Discharging device: such as support frame, roll turning device.
- Safety devices: emergency stop button, protective cover, displacement detection system, etc.
3. Working principle of four-roller plate bending machines
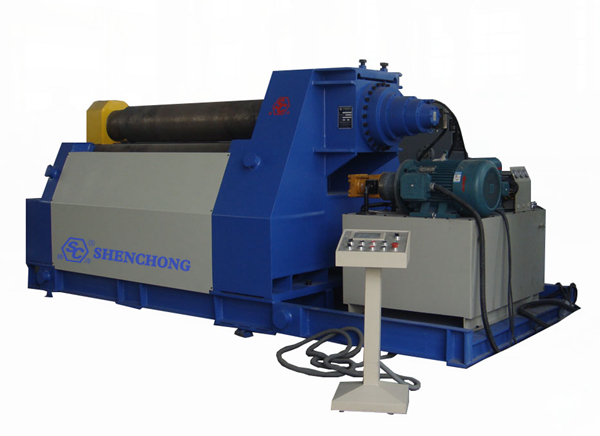

The 4 roller plate rolling machine is an advanced plate forming equipment. Its working principle is to make the plate produce plastic deformation under the action of mechanical and hydraulic pressure through the coordinated action of four working rollers (upper roller, lower roller, left roller, right roller), so as to achieve automatic pre-bending and precise rolling. The following will analyze its working principle in detail from the aspects of structure, process, force, control, etc.
1) Sheet feeding
- The sheet is fed from the side or front through the feeding platform.
- After aligning the center, it is clamped and positioned by the upper and lower rollers.
2) Sheet clamping
- The lower roller rises and presses the sheet tightly under the upper roller.
- The initial clamping state is formed and ready for rolling.
3) Sheet pre-bending (eliminating residual straight edges)
- Lift the side roller on one side (such as the left roller).
- One end of the sheet is lifted up, forming a three-point force with the upper and lower rollers, causing it to be partially bent (pre-bent).
- The sheet rotates and repeats the operation on the other end to achieve pre-bending at both ends.
- This method greatly reduces the residual straight edges and improves the forming quality.
4) Sheet rolling
- The side rollers are gradually raised (programmable curvature control).
- The sheet is continuously rolled into an arc or cylinder in the three-point bending mode.
- The drive roller continuously drives the sheet forward to form a complete circular cross-section.
5) Sheet unloading
- After the rolling is completed, the upper roller can be flipped or moved sideways.
- The formed workpiece is unloaded by hydraulic or mechanical auxiliary mechanisms.
- Can directly proceed to the next welding or rounding process.
4. Force analysis of four-roller plate rolling
The force analysis of the four-roller plate rolling machine is the core part of understanding its rolling mechanism, controlling accuracy and optimizing the forming process. The advantage of the four-roller structure in terms of force is that it can form a more ideal three-point bending system, effectively control the deformation process of the plate, and improve the quality of pre-bending and rolling.
1) Main stress points of 4 roller plate rolling machine
During the rolling process, the plate is mainly subjected to the following forces:
- Upper roller pressure: applies the main bending force to the plate to make it plastically bent.
- Lower roller support force: clamps the plate with the upper roller, and provides support and transmission at the same time.
- Side roller top pressure: controls the curvature and shape accuracy during pre-bending and rolling.
- Friction: comes from the friction between the upper/lower roller and the plate, used to drive the plate to move.
- Slab rebound force: the elastic recovery force of the plate after bending, which is an important factor affecting the accuracy.
2) Analysis of the force process stage
Initial clamping stage:
- The plate is placed between the upper and lower rollers.
- The lower roller rises and applies pressure, forming a clamping force with the upper roller, generating normal pressure.
- The friction between the upper/lower rollers controls the movement of the plate.
Pre-bending stage:
- One side roller rises, forming a three-point force with the upper and lower rollers.
- The end of the plate is bent, and a plastic deformation zone is formed locally.
- The bending moment is generated below the mid-axis of the plate thickness, forming an asymmetric stress distribution.
Rolling stage:
- The plate is subjected to force between three fulcrums (upper roller + two side rollers).
- It is squeezed and bent while moving forward continuously, forming a continuous curve.
- The bending radius is determined by the position of the side rollers, and the pressure distribution must be uniform.
During the bending process, the stress state inside the plate is:
- The upper surface is tensile, and the stress is positive.
- The lower surface is compressed, and the stress is negative.
- The stress at the neutral axis is zero, and bending occurs but no elongation occurs.
3) Strength advantages of the four-roller structure
Comparison items | Three-roller plate rolling machine | Four-roller plate rolling machine (advantages) |
Support point | 2 sides + 1 center | True three-point forming structure |
Sheet stability | The plate is easy to slide | Stable plate fixing and clamping |
Rolling accuracy | General | High (controllable bending moment adjustment) |
Pre-bending ability | Weak | Strong (structure supports positive and negative pre-bending) |
Rebound control | Difficult to control accurately | Programmable compensation + dynamic adjustment |
5. Rolling control method
With the development of technology, the plate rolling machine has gradually transitioned from traditional manual/hydraulic control operation to electronic numerical control (NC) and computer numerical control (CNC) systems, achieving a higher level of intelligent manufacturing. It is the rolling control method of the 4 roller plate rolling machine that determines its forming accuracy, operating efficiency and automation level.
1) Roller position control (displacement control)
- Control the lifting and lowering displacement of the upper roller, lower roller, left and right side rollers
- Determine the bending radius and pressure area of the plate during the forming process
- Usually, the closed-loop control is completed by the hydraulic proportional valve + displacement sensor
2) Rolling trajectory control
- Control the moving trajectory of the side roller (oblique line, curve)
- Achieve complex shapes (such as conical cylinders) or multi-segment arc rolling
- The trajectory is usually pre-programmed by the CNC system
3) Clamping control
- Control the clamping pressure of the upper and lower rollers on the plate
- Ensure that the plate does not slip during the rotation
- Corresponding to different materials Dynamic adjustment of quality and thickness
4) Drive control (speed adjustment)
- Control the rotation speed of the roller to achieve smooth feeding
- Advanced control system can adjust the acceleration and deceleration during the rolling process
- Important to prevent material tearing, overpressure or surface damage
5) Programmed control (automatic logic)
Multiple rolling steps are preset in the control system:
- Plate positioning
- Automatic clamping
- Pre-bending the first end
- Plate rotation
- Pre-bending the second end
- Full circle rolling
- Unloading, etc.
Users only need to enter parameters such as plate thickness, material, and roll diameter, and the system automatically adjusts the position and movement of each roller.
6. Analysis of the advantages of four-roll plate rolling machine
4- roll plate rolling machine is widely used in modern sheet metal forming manufacturing, mainly because its structure and control system bring many advantages. Compared with traditional equipment such as three-roll plate rolling machine and symmetrical plate rolling machine, 4 roller plate rolling machine has obvious advantages in accuracy, efficiency, operability and so on.
1) Structural advantages of 4 roller plate rolling machine
- Four-roller structural design: active upper roller + lower roller clamping + double-side roller adjustment, more stable structure. Supports symmetrical rolling and asymmetrical pre-bending
- Lower roller fixed plate: the plate is always on the fixed roller, not easy to slide, easy to position and control accuracy.
- No need to flip the plate: Unlike the three-roller machine, the plate is always processed on the same side during the entire rolling process, without turning around.
2) Process and operation advantages
- One-time forming: pre-bending + rolling can be completed in the same process cycle, reducing manual and positioning errors.
- Strong pre-bending ability at both ends: the left and right side rollers can be raised and lowered respectively, and can independently perform precise pre-bending on both ends (almost no straight edges).
- Adapt to conical rolling: the side roller trajectory can be adjusted programmably, suitable for non-circular structures such as conical cylinders and ellipses.
- Easy to operate: Most four-roller plate rolling machines are equipped with CNC systems (NC/CNC), and users only need to enter parameters to operate.
- Adapt to a wide range of plate thicknesses: various metal plates with thicknesses ranging from 1mm to more than 100mm (depending on the model) can be rolled.
- Lower operator requirements: Compared with the three-roller plate rolling machine, it has low technology dependence, is easy for novices to get started, and is safer.
3) Advantages of forming quality
- Higher roundness: The multi-point force control accuracy is high, and the roundness and cylindricity of the rolled forming are better than those of the three-roller.
- Good rebound control: The side roller force is continuously controllable, which can reduce elastic rebound and improve rolling accuracy.
- Good surface quality: The plate is not easy to slide, does not need to be flipped, and scratches, creases and other defects are avoided.
- More precise edge docking: The straight edge is small, which is conducive to subsequent automatic welding, seam docking and other precision operations.
4) Production efficiency and automation advantages
- Fully automatic control system: supports NC/CNC programming, has memory storage function, and is suitable for mass production.
- Reduced process time: All steps are completed in one positioning, shortening the total processing time by 30%–50%.
- Suitable for automated production lines: It can link loading and unloading systems, robots, welding stations and other equipment.
- Support remote monitoring/diagnosis: Some high-end equipment can be connected to the Internet to achieve industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) access.
5) Comparison of typical advantages of three-roller plate rolling machine
Comparison items | Three-roller plate rolling machine | Four-roller plate rolling machine (advantages) |
Pre-bending function | Requires multiple flips, large straight edges | Automatic pre-bending, extremely short straight edge (≤1.5 times the plate thickness) |
Centering and positioning | Relies on manual experience for positioning | The plate is fixed on the lower roller and automatically centered |
Rolling efficiency | Many processes, low efficiency | All rolling processes are completed in one go |
Conical rolling capacity | Structural limitations make it difficult to achieve | Adjustable roller trajectory, free control of cone angle |
Operational technical difficulty | High, requires skilled workers | Low, friendly CNC interface, easy to train |
7. How to choose a four-roll plate rolling machine?
Purchasing a 4-roll plate rolling machine is an important equipment investment decision, which is directly related to production efficiency, processing accuracy and the long-term development ability of the enterprise. The following is a systematic and practical “4 roller plate rolling machine purchase suggestions and guidelines” to help you scientifically select according to actual needs and avoid unnecessary waste and hidden dangers.
1) Clarify your application requirements
Before selecting a model, you must be clear about your workpiece characteristics and production methods:
Key parameters | Considerations |
Sheet thickness | Maximum/minimum processing plate thickness range (affects upper roller diameter and hydraulic system) |
Sheet width | Maximum processing width, determines machine body width and rigidity requirements |
Material type | Plain carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, wear-resistant steel, etc., affect pressure and forming radius |
Minimum roll diameter | Required minimum inner diameter? Involves bending capacity and roller arrangement |
Workpiece type | Cylinder, cone, ellipse, non-standard parts? Affects control system and side roller trajectory design |
Batch size | Single-piece customization or large batch? Determine whether to equip with CNC or automatic loading and unloading device |
2) Recommendations for selecting main technical parameters
- Upper roller diameter: should be large enough to withstand the maximum bending force and avoid deflection; affected by the thickness of the rolled plate.
- Lower roller and side roller diameter: affects the stable clamping and bending effect, and the symmetrical structure is better.
- Hydraulic system pressure: the higher the pressure, the stronger the processing capacity, but the cost also increases.
- Motor power: directly determines the plate driving capacity and processing speed.
- Roller pitch and roller arrangement: determine the forming quality and the minimum roll diameter. Eccentric side rollers are suitable for cone rolling.
- Control mode: NC is suitable for conventional applications, CNC is suitable for complex and high-precision scenarios.
- Machine structure material: high-strength cast steel or welded structure to ensure long-term deformation resistance.
3) Brand and after-sales recommendations
Choosing a reliable manufacturer and perfect after-sales support is the key.
- Give priority to well-known brands or manufacturers with good industry reputation: equipment quality is guaranteed and key components have a long life.
- Inspect the manufacturer’s assembly and trial machine site: see the actual rolling effect and understand the operability of the control system.
- Ensure that the supplier provides installation, commissioning and training services: shorten the machine cycle and improve production efficiency.
- Understand the after-sales response time and parts support: Timely maintenance is extremely important when equipment fails.
4) Summary of the selection ideas for 4 roller plate rolling machine
You can use the following table to organize your needs and communicate with the manufacturer:
Item | Data or requirement description |
Maximum plate thickness | For example, 20mm Q345 steel |
Plate width range | 2000mm |
Minimum inner diameter | 400mm |
Workpiece type | Cylinder + cone |
Processing material | Mixed stainless steel and carbon steel |
Control method | NC or CNC |
Batch or not | Yes, it is recommended to configure a feeding device |
Installation location restrictions | Width/height/foundation load-bearing requirements, etc. |