Table of Contents
A combined punching and shearing machine is a multi-station hydraulic processing equipment that integrates multiple metal profile processing functions into one machine. It is widely used in industries such as steel structures, iron towers, power, bridges, and machinery manufacturing.
So, how should we correctly use and operate a combined punching and shearing machine? Below is the 2026 Combined Punching and Shearing Machine Operation Guide.
1. Combined Punching And Shearing Equipment Introduction
The combined punching and shearing machine is a multi-station metal processing equipment integrating punching, shearing, corner cutting, and grooving functions. It is commonly used for the rapid processing of profiles and plates such as angle steel, flat steel, channel steel, and steel plates.
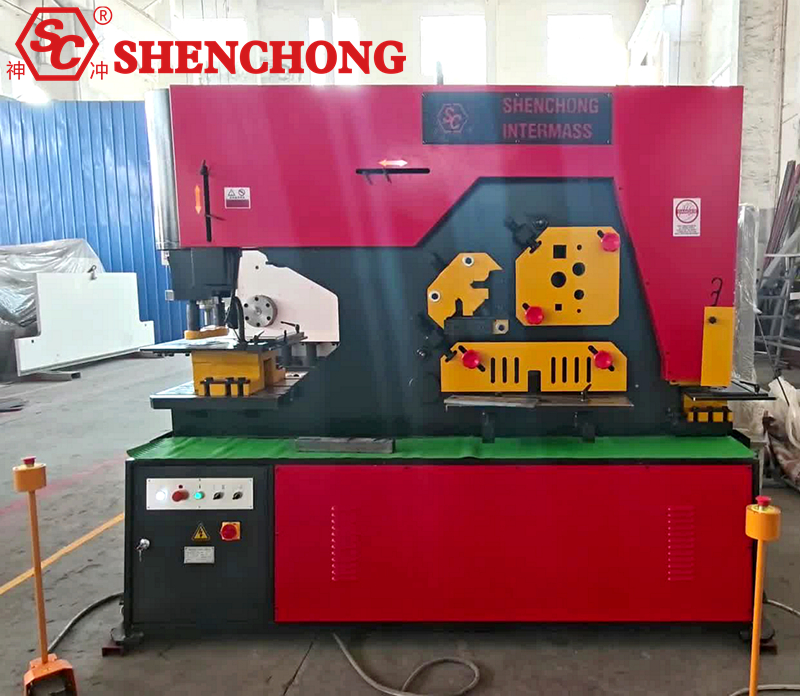

1) Main Stations
- Punching station
- Section cutting station
- Angle Cutting station
- Shearing station
- Notching station
2) Widely Used in
Steel Structures, Power Towers, Engineering Machinery, Building Hardware, Shelving, Bridge Components, etc.
3) Basic Structural Components
Frame System: High-strength welded or cast steel structure
Hydraulic System: Oil tank, oil pump, motor, valve group, cylinder
Working Mechanism of hydraulic ironworker:
- Punching slider
- Shearing slider
- Pressure device
Electrical Control System: Buttons, foot pedal, emergency stop
Positioning System: Baffle, straightedge, scale
Safety Protection Devices: Protective cover, limit switch, emergency stop
4) Key Advantages and Features
- Multi-functional: Reduces the number of machines and floor space required
- High efficiency: No need for frequent machine or workstation changes
- Simple operation: Easy for ordinary workers to operate
- Stable structure: Hydraulically driven, high punching and shearing force
- Convenient maintenance: Standardized molds, easy to replace
2. Pre-Start Preparation and Inspection (Standard Procedure)
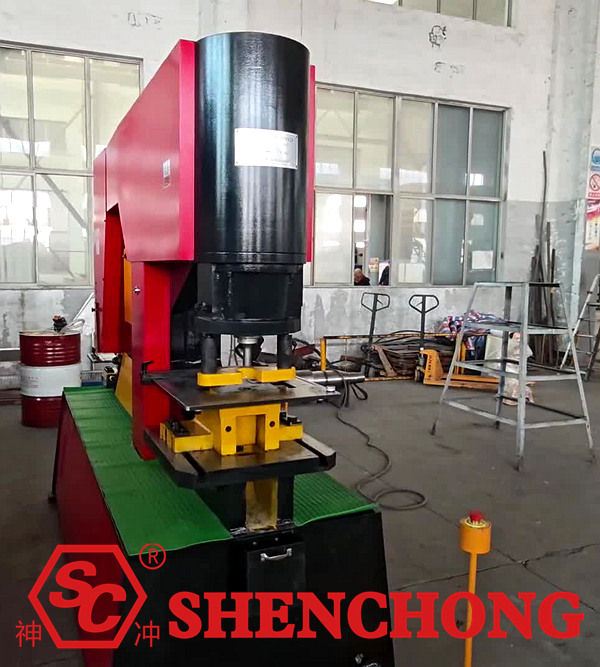

Environmental Inspection:
- Ground is level and free of oil stains.
- No obstructions nearby.
- Adequate lighting.
Electrical System Inspection:
- Power supply voltage meets requirements.
- Grounding wire is reliable.
- Control buttons are not stuck.
Hydraulic System Inspection:
- Oil level: above the center line of the oil gauge.
- Oil quality: no emulsification, no impurities.
- Oil pipes and joints are leak-free.
Mold and Cutting Tool Inspection:
- Punch and lower die are securely installed.
- Shear gap is normal.
- Cutting edge is sharp and without chipping.
Safety Device Confirmation:
- Emergency stop button is effective.
- Protective covers are complete.
- Foot pedal anti-accidental activation device is normal.
3. Detailed Operating Procedures for Each Workstation
1) Detailed Operation of the Punching Workstation
Die Selection:
- Punch diameter ≥ Material thickness × 2
- The thicker the material, the larger the hole diameter should be.
Installation Steps:
- Install the punch.
- Install the lower die.
- Tighten the locking bolts.
- Manually test the pressure to confirm concentricity.
Positioning and Punching:
- Adjust the baffle to determine the hole spacing.
- Keep the workpiece close to the positioning surface.
- Confirm that both hands are away from the die.
- Start the punching action.
Precautions:
- Stacked materials are not allowed for punching.
- Do not punch quenched or high-strength materials.
- Scrap materials must be cleaned up promptly.
2) Detailed Operation of Shearing Station
Shearing Preparation:
- Confirm material thickness ≤ rated capacity.
- Adjust the height of the pressure device.
Shearing Steps:
- Feed material smoothly.
- Align with shearing marks.
- Start shearing.
- Remove material after shearing.
Shearing Quality Requirements:
- Straight cut
- Minor burrs
- No obvious twisting
3) Angle Steel Cutting Station
- Angle steel close to the positioning surface.
- Ensure the flange is perpendicular to the blade.
- Complete shearing in one pass.
- Check the integrity of the cross-section.
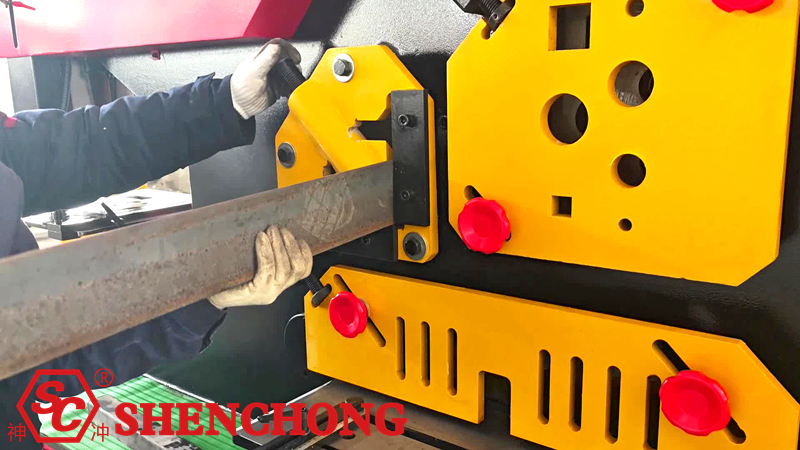

4) Corner Cutting/Notching Station
- Strictly use the corresponding mold.
- Do not substitute.
- Try cutting one piece before each processing.
4. Basic Operating Procedures Of Ironworker
1) Power On
- Turn on the power switch.
- Start the hydraulic system.
- Run the machine unloaded 1-2 times to confirm smooth operation and no abnormal noise.
2) Punching Operation
- Select the appropriate punch and lower die.
- Adjust the positioning baffle to ensure accurate hole positioning.
- Place the workpiece, ensuring it is flush against the positioning surface.
- Confirm your hands are away from the die.
- Depress the foot pedal or press the button to complete the punching operation.
Note:
- Punching of excessively thick or high-strength materials is strictly prohibited.
- Punching waste should be cleaned up promptly.
3) Shearing Operation (Shearing Plates/Profiles)
- Adjust the pressure device according to the material thickness.
- Flush the workpiece against the ruler or baffle.
- Align the shearing line.
- Start the shearing operation.
- Remove the workpiece after shearing.
Note:
- Do not shear materials exceeding the equipment’s rated capacity.
- Do not force shearing by feeding at an angle.
4) Corner Cutting/Notching (if configured)
- Select the corresponding die.
- Confirm the workpiece placement direction.
- Complete the processing in one operation.
- Check the cut quality.
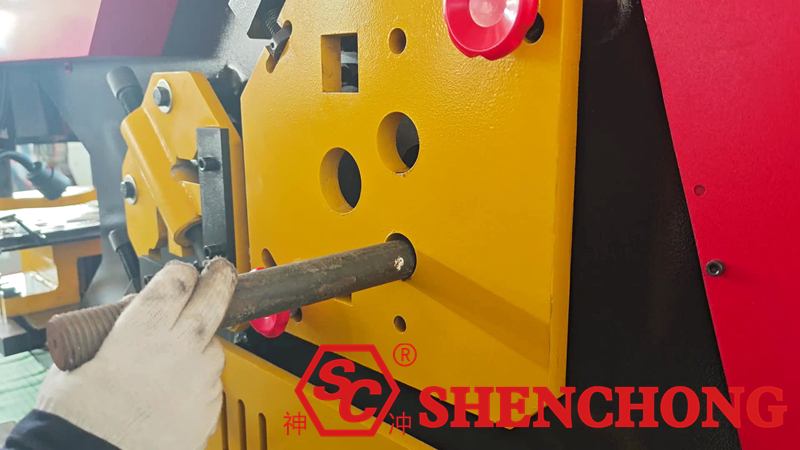

5. Safety Operating Points (Important)
- Never put your hands into the mold area.
- Never operate one machine simultaneously by two people.
- Never wear gloves during punching operations.
- Always wear safety goggles during processing.
- Stop the machine immediately if any abnormality is found.
6. Shutdown Procedure
- Shut down the hydraulic system.
- Disconnect the main power supply.
- Clean the worktable and waste materials.
- Apply anti-rust oil to the mold (for long-term shutdown).
7. Daily Maintenance Points
- Check the hydraulic oil level every shift.
- Regularly check the mold wear.
- Sharpen or replace dull shears promptly.
- Run the machine unloaded before starting formal processing if it will not be used for a long time.
8. Combined Punching And Shearing Machine Brief Troubleshooting of Common Problems
Problems | Possible causes |
Large punching burrs | Punch dulling / improper clearance |
Incorrect shearing cut surface | Insufficient cutting tool wear / insufficient material clamping |
Weak action | Insufficient hydraulic oil / too low pressure |
Abnormal noise | Loose fasteners / insufficient lubrication |