Table of Contents
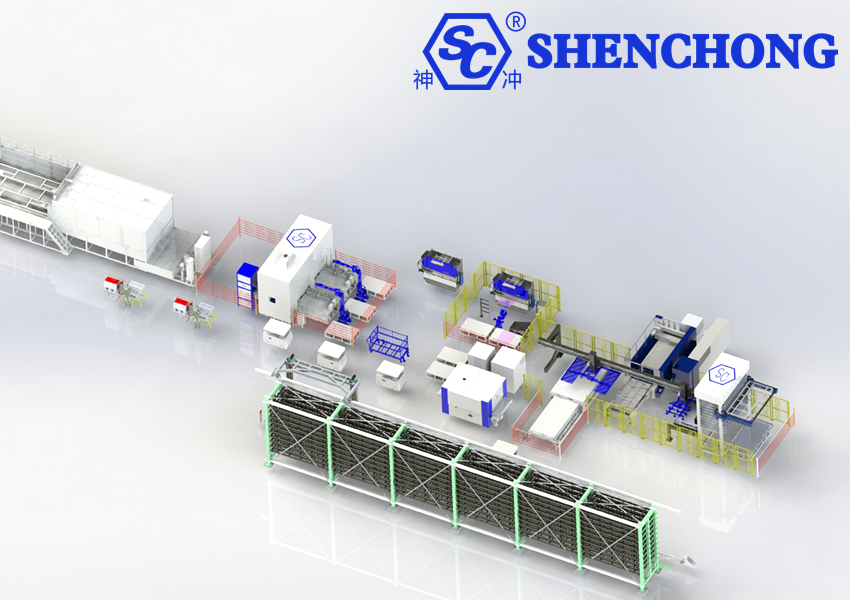
An automatic combined row sheet metal storage system essentially connects multiple sets (rows) of three-dimensional sheet metal racks in parallel. Through a unified automated handling and control system, it enables centralized and efficient sheet metal storage and retrieval. Compared to single-row systems, it is more suitable for sheet metal factories with a wide variety of sheet metal products, frequent material usage, and multiple production lines.
1. Definition of a Combined Row Sheet Metal Automated Storage System
A combined row sheet metal storage system is an automated storage solution that utilizes two or more rows of three-dimensional sheet metal racks arranged side by side (tandem), managed by a single automated handling and control system. This system enables centralized, high-density storage of sheet metal, automated loading and unloading, and rapid dispatch to processing equipment.
Its core features include:
- Multiple rows of racks share shared handling aisles and equipment
- Unified information management and scheduling
- Capable of simultaneously feeding multiple production lines.
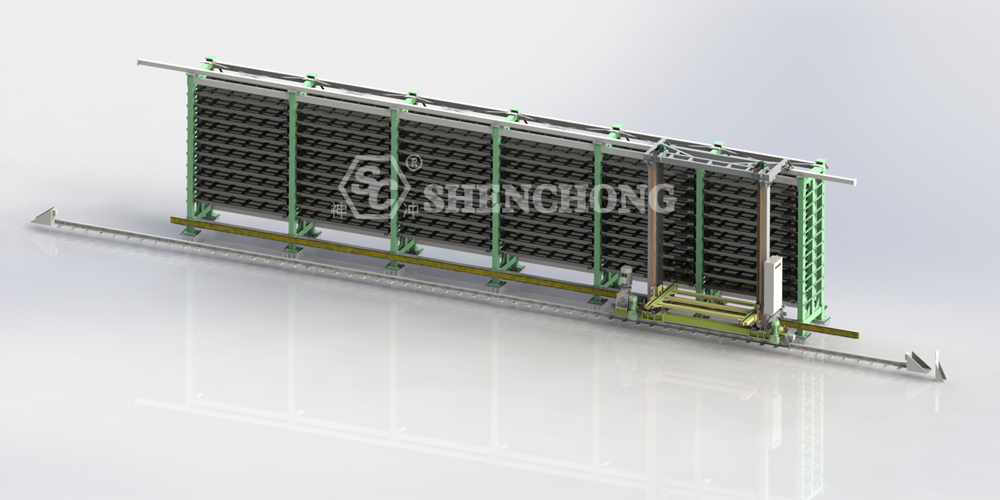
2. Components of Combined Row Sheet Metal Automated Storage System
The Combined Row Sheet Metal Storage System can be divided into four major modules: storage structure, handling system, control system, and safety protection. Each module includes several key components:
1) Storage Structure
Multi-Row Shelf:
- Arranged in two or more rows, either in a straight or back-to-back configuration.
- Multi-layered shelves, each capable of storing entire packages of sheet metal (e.g., 3000 x 1500 mm, 4000 x 2000 mm).
- High-strength steel structure, heavy-load-resistant and deformation-resistant.
Pallet Unit:
- Specialized steel pallets carry sheet metal for automated handling and handling.
- Compatible with sheet metal of varying thicknesses and materials.
Aisles and Support Structure:
- Transport aisles or central aisles are provided between rows for automated handling equipment.
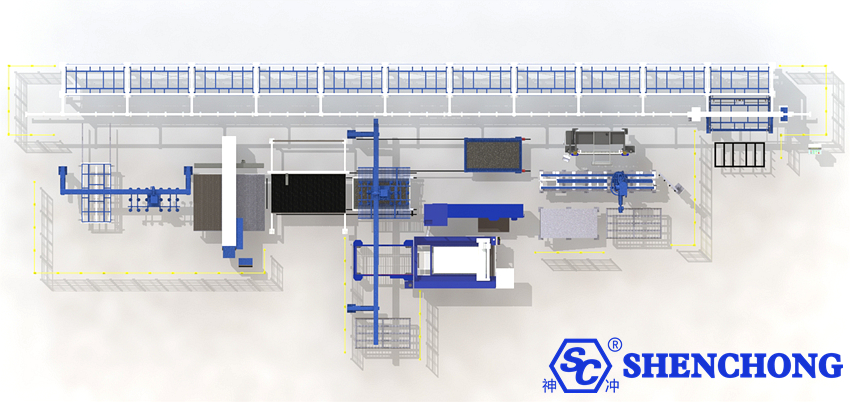
2) Automated Handling System
Transport Trolley/Gantry Carrier:
- Operates between or in front of the tank racks, picking up and placing pallets.
- Supports lateral, longitudinal, and vertical movement.
Lifting Device:
- Enables loading and unloading of sheets between shelves.
Telescopic Arm/Vacuum Suction Cup:
- Reaching into shelves to pick up or place pallets.
- Suction cups are suitable for protecting sheet surfaces from scratches.
Conveying and Docking Unit:
- Delivers sheets to the loading platform of equipment such as laser cutters and press brakes.
3) Control and Information Management System
PLC Control Cabinet:
- Controls the movement of handling equipment, lifting mechanisms, and conveying devices.
WMS Warehouse Management System:
- Manages inventory, records inbound and outbound information, and generates task instructions.
MES/ERP Interface:
- Interfaces with the production management system to enable automatic material handling according to production plans.
HMI Operation Terminal:
- Human-machine interface, allowing operators to manually or automatically execute inbound and outbound tasks.
4) Safety and Inspection System
- Photoelectric Sensor: Detects the presence of pallets in shelves to prevent misoperation.
- Weight Detection: Prevents overloaded equipment from operating.
- Anti-Collision Device: Prevents collisions between handling equipment and people or objects during operation. Safety door and emergency stop button: Ensure personnel safety during maintenance.
- Environmental monitoring (optional): Monitors temperature, humidity, smoke, and other factors to prevent environmental factors from affecting panel quality.
3. Working Principle of muti-raw sheet metal storage system
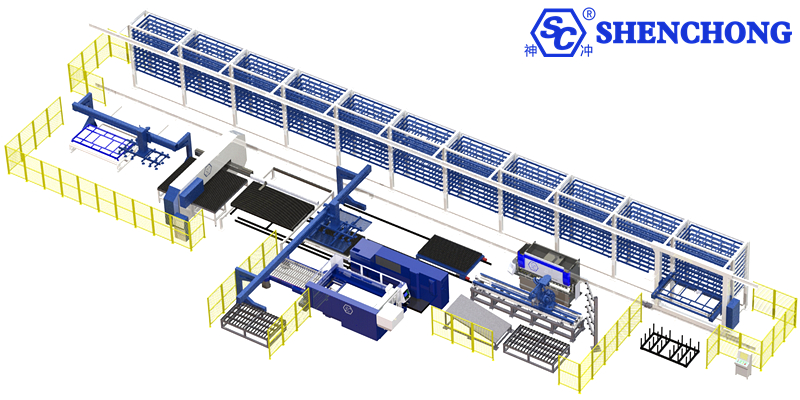
The operating principle of the automated combined row sheet metal storage system can be understood as “centralized multi-row storage + unified handling channels + intelligent scheduling control.” Automatic handling equipment operates between multiple rows of three-dimensional racks, enabling automated inbound, outbound, and coordinated multi-row feeding of sheets.
1) Inbound Process
Sheets arrive at the inbound location:
- A forklift, loading platform, or conveyor delivers the entire package of sheets to the inbound workstation.
Information Entry:
- Sheet material, thickness, specification, batch, and other information are scanned or manually entered.
Automated Inbound:
- A transport trolley/crane operates from the central aisle to the inbound location and grabs a pallet.
- It then ascends to the designated level, and a telescopic arm/suction cup pushes the pallet into the designated bay.
2) Storage Management
Location Allocation:
- The WMS automatically allocates bays based on sheet type, thickness, and frequency of use.
Inventory Monitoring:
- The status of each bay (empty/full, sheet information) is updated in real time in the system database.
Optimized Placement:
- Frequently used sheets are placed near the outbound shelf or on lower levels to reduce retrieval time.
3) Outbound Process
Production Task Issuance:
- The MES/ERP system transmits sheet demand information to the warehouse system.
System Scheduling Handling Equipment:
- Automatically calculates the optimal route and determines the order in which sheets are retrieved.
Sheet Outbound:
The handling equipment drives to the target shelf → raises and lowers to the corresponding level → grabs the pallet → delivers it to the loading platform or outbound exit of the processing equipment.
Multi-Row Collaboration:
- The handling equipment can switch between multiple rows of shelves to retrieve materials, enabling multi-tasking.
4) Core Control Logic
- Centralized Control: Multiple rows of shelves share a single handling equipment and control system, reducing investment costs.
- Intelligent Scheduling: The system optimizes routes based on task priority, shelf distance, and equipment operating status.
- Information Traceability: Every entry, exit, and transfer is recorded to prevent material errors and omissions.
4. Advantages of a Row-and-Row Automated Sheet Metal Storage System
The advantages of a combined row sheet metal storage system primarily lie in space utilization, efficiency, flexibility, and management capabilities.
Common core advantages are as follows:
1) High Space Utilization
- The row-and-row layout allows for the side-by-side placement of multiple vertical racks, sharing rails and handling equipment, reducing aisle occupancy.
- Sheet metal sheets are stored vertically in stacks, achieving three-dimensional storage, which can increase storage density by 3-5 times compared to traditional floor stacking.
2) Improved Storage and Retrieval Efficiency
- Automated lifting and horizontal transfer devices quickly deliver target trays to the access point.
- The multi-row layout enables parallel multi-tasking, reducing wait times.
- Seamlessly integrates with CNC processing equipment (laser cutting machines, press brakes, etc.), supporting automated loading and unloading, saving manual handling time.
3) Flexible Management
- Supports mixed storage of sheets of varying sizes, thicknesses, and materials, managed by zoning using trays or pallets.
- The system is scalable, allowing for the addition of row-and-row modules to the existing system as production capacity demands change.
4) Safety and Protection
- Automated operation reduces direct contact with heavy sheet metal, lowering the risk of work-related injuries.
- The system features anti-tipping, anti-collision, and position detection functions to ensure the safety of both equipment and personnel.
5) Intelligence and Visualization
- Equipped with a warehouse management system (WMS), it enables real-time updates of sheet metal inventory, batch traceability, and inventory alerts.
- Interconnection with ERP/MES systems streamlines production planning and warehouse management.
- Optional barcode and RFID recognition technologies automatically identify sheet metal information.
6) Reduced Operating Costs
- Reduces labor and forklift handling costs, reducing sheet metal waste.
- Improve the efficiency of integrated warehousing and production, shorten production cycles, and reduce overall production costs.
5. Summary
Combined row sheet metal storage system = multi-row three-dimensional racking + automated handling mechanism + centralized control system
“Combined Row” means that multiple rows of racks share the same track, control system, and handling mechanism. This system enables multi-row, multi-layer, high-density sheet metal storage and can directly interface with multiple processing equipment.
The core components of the multi-row automated sheet metal storage system are:
Multi-row three-dimensional racking (storage) + automated handling devices (pick-and-place) + an information control system (scheduling) + a safety protection system (operational assurance).
The automatic combined row sheet metal storage system operates by sharing handling channels and a unified control system, allowing multiple rows of racks to operate as a single warehouse, achieving high-density storage and efficient retrieval of sheet metal.
Combined row sheet metal storage system advantages
- High Density: Multiple rows and multiple layers increase storage capacity per unit area by 3-6 times.
- Multi-Equipment Interaction: Can simultaneously feed multiple production lines.
- High Efficiency: A single handling mechanism can manage multiple rows of racks, saving equipment investment.
- Information: Inventory is tracked in real time, with automatic recording of incoming and outgoing goods.
- Flexible Layout: Can be arranged in a straight row, back-to-back, or in a “U-shaped” configuration surrounding the production line.