Table of Contents
Robotic sheet metal bending refers to automated sheet metal bending operations performed by industrial robots in conjunction with CNC press brake bending machines. It is a crucial component of intelligent sheet metal manufacturing, significantly improving production efficiency, bending accuracy, and safety.
1. Robotic Bending System Overview
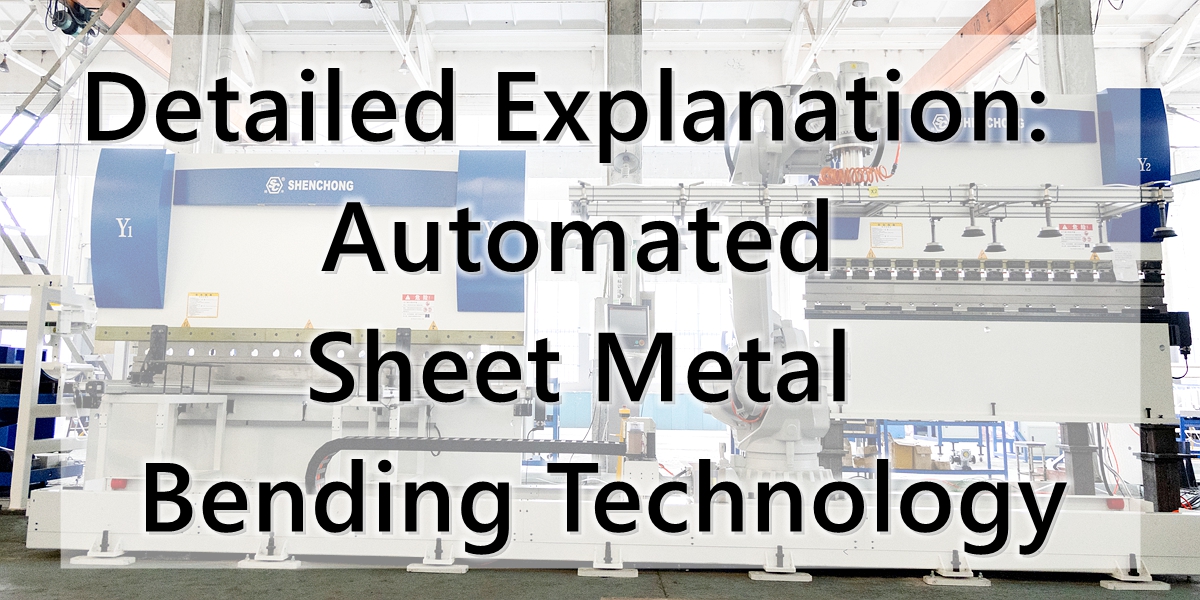
A robotic sheet metal bending system is a comprehensive automated unit composed of the following parts:
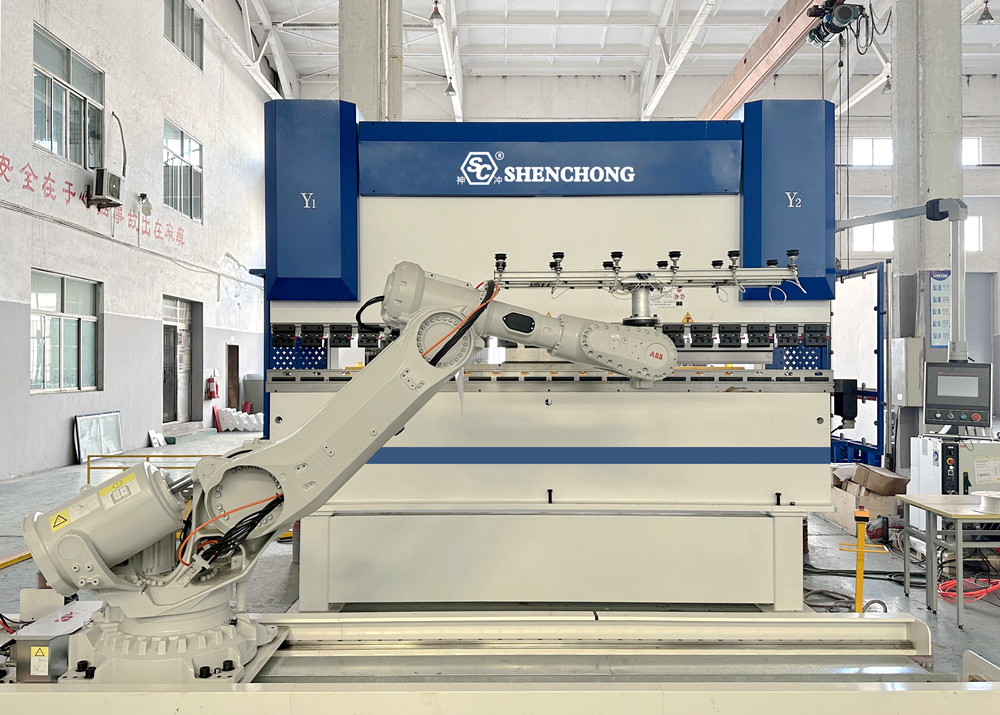

- CNC Press Brake: Typically a servo or hydraulic press brake with angle detection and compensation functions.
- Industrial Robot: Responsible for gripping, positioning, flipping, feeding, and unloading materials. Six-axis robots are commonly used (e.g., KUKA, ABB, Yaskawa, etc.).
- End Gripper (Gripper): Designed specifically for sheet metal parts, employing vacuum suction cups, electromagnetic adsorption, or mechanical clamping.
- Vision Positioning System (Optional): Used for automatic sheet metal alignment and hole position recognition.
- Bending Control Software and Coordination Control System: Enables synchronization of the bending machine and robot movements, path planning, and bending sequence control.
2. Robotic Sheet Metal Bending Workflow
1) Sheet Material Feeding
Robot Actions: Grabs metal sheets from the rack, pallet, or loading table.
Common Grippers: Vacuum suction cups, magnetic suction devices, or mechanical grippers.
Key Functions:
- Automatic sheet position detection (via positioning pins or vision system)
- Automatic sheet size and orientation recognition
- Avoids multiple sheet pickups (vacuum detection)
2) Sheet Material Positioning & Alignment
Purpose: To ensure the sheet material is accurately placed into the bending machine’s working area.
Implementation Methods:
- Using positioning blocks (mechanical limiters)
- Vision positioning system (identifying hole positions or edges)
- Automatic adjustment of the bending machine’s back gauge
Control Points: The robot and bending machine back gauge coordinate systems must be strictly calibrated.
3) Feeding to Press Brake
Robot Actions: Feeds the sheet material along a predetermined path between the upper and lower dies of the bending machine.
Synchronous Control: Before the upper die of the bending machine descends, the robot remains stationary and releases appropriate clamping pressure.
Communication: The robot and bending machine are linked in real time via I/O or fieldbus (such as PROFINET, EtherCAT).
4) First Bending
Bending Machine Actions: Completes the first bending angle according to the set program.
Robot Actions:
- Maintains workpiece stability
- Appropriately retracts after bending to prevent interference
- Monitors workpiece deformation
5) Flipping & Repositioning
Robot Actions: Adjusts the sheet metal posture (flipping, rotating, or tilting) according to the bending sequence.
Typical Operations:
- Upward flipping, downward flipping, side flipping
- Secondary bending angle adjustment
- Multiple bending operations in conjunction with the bending machine
Key Control Points: Path planning to avoid collisions, smooth posture switching.
6) Multi-step Bending Cycle
The system repeats the cycle of “feeding—bending—flipping—repositioning”.
The system automatically identifies the bending sequence and optimizes the robot path.
The bending angle is controlled by the bending machine’s CNC program; the robot is only responsible for workpiece positioning and clamping.

7) Unloading
Robot Action: Places the bent workpiece into the finished product area, conveyor line, or pallet.
Optional Functions:
- Finished product inspection (dimensions, angles)
- Automatic stacking or sorting
- Connection with subsequent processes (e.g., welding, grinding)
8) System Cycle & Monitoring
Automatic cyclic production: Once the bending process of one workpiece is completed, the robot automatically starts the next one.
Control System:
- Robot and bending machine linkage control
- Real-time monitoring of equipment status and alarms
- MES system data upload (production batch, cycle time, pass rate)
3. Technical Characteristics of Robotic Bending of Metal Sheets
The sheet metal robotic bending system integrates an industrial robot, a CNC press brake bending machine, and a vision positioning and intelligent control system, enabling fully automated, high-precision, multi-process sheet metal bending. Its core technical characteristics are reflected in the following aspects:
1) High-Precision Bending Control
Robot repeatability: ±0.05 mm ~ ±0.1 mm
Bending angle accuracy: ±0.2° ~ ±0.5°
With the bending machine’s angle compensation and automatic detection system, closed-loop precision control can be achieved.
Real-time monitoring of bending force and angle feedback automatically corrects errors.
2) Intelligent Path Planning and Attitude Control
Offline programming software (such as RobotStudio, KUKA.Sim, RoboDK) automatically generates the bending path.
Intelligent obstacle avoidance algorithms ensure collision-free operation between the robot and the mold, sheet metal, and machine body.
Multi-axis coordinated control enables complex actions such as sheet metal flipping, rotation, and repositioning.
Digital twin simulation is used to verify the bending process in advance.
3) Flexibility and Rapid Switching
Programmed control allows for rapid switching between bending tasks for different parts.
Die, fixture, and robot parameters can be automatically recalled.
Suitable for multi-variety, small-batch, or mixed-line production.
Integrates with MES systems for automated task scheduling.
4) Automated Loading and Unloading
The robot completes the entire process of loading → bending → unloading via suction cups or electromagnetic grippers.
Features automatic detection of sheet metal position, thickness, and shape.
Integrates with automated material handling systems, AGVs, or conveyor systems for unmanned operation.
5) Safety and Collaborative Control
The bending machine and robot achieve synchronized movements via bus communication (EtherCAT / PROFINET / Modbus).
Equipped with multi-level protection including safety light curtains, laser scanners, fences, and access control interlocks.
The control system features emergency stop and anti-collision logic.
The Human-Machine Interface (HMI) displays bending status and alarm information in real time.
6) Data-Driven and Visualized Management
Real-time collection of data such as bending force, angle, and cycle time.
Traceability of production batches, operators, and bending parameters.
Integration with ERP/MES systems for digital factory management.
Can be equipped with AI algorithms to analyze production efficiency and energy consumption.
7) Energy-Saving and Reliable Design
Servo hydraulic or all-electric bending machines offer 30%–50% energy savings.
Long continuous operating life of the robot, with a maintenance cycle of 3–5 years.
The system can operate continuously for 24 hours without human intervention, exhibiting high stability.
Typical performance parameter table (for reference):
Item | Contents |
Bending accuracy | ±0.2°~±0.5° (depending on machine model and vision system) |
Sheet metal dimensions | 300×300mm ~ 2500×1500mm (customizable) |
Sheet thickness range | 0.5~6mm (commonly used steel, aluminum, stainless steel) |
Bending machine tonnage | 80~250 tons (common) |
Robot load | 20~500 kg (depending on plate thickness and size) |
Automation level | Single-machine automatic, flexible production line, and unmanned production line are available. |
Programming process | Bending path generated via offline programming software. |
Safety configuration | Laser protection, gratings, fences, interlocking doors, etc. |
4. Advantages of Robotic Metal Sheet Bending Systems

The robotic sheet metal bending system deeply integrates CNC bending machines with industrial robots and intelligent control systems, achieving automation, flexibility, and intelligence in the sheet metal bending process. This system offers significant advantages over traditional manual bending in terms of efficiency, precision, safety, flexibility, and management.
1) Automated Production, Increased Efficiency
The robot can perform continuous bending 24 hours a day without human intervention.
Multiple bending operations are completed in one pass, significantly reducing workpiece handling and positioning time.
High cycle time per piece and reduced manual operation steps can increase production efficiency by 30%–50%.
It can be integrated with loading racks, automated warehouses, and AGV logistics systems to form a fully automated production line.
2) High Precision and Consistency
The robot has high positioning accuracy (±0.05 mm), and bending angle errors can be controlled within ±0.2°.
Automatic angle compensation and back gauge correction ensure consistent product quality for every piece.
It eliminates errors, fatigue, and reliance on experience inherent in manual operation.
3) Flexible Production, Adaptable to Multiple Varieties
Supports automatic identification and rapid changeover of various workpieces.
New workpiece bending programs can be quickly generated via offline programming software.
Automatic switching of parameters such as molds, fixtures, and paths supports flexible manufacturing of small batches and multiple varieties.
Suitable for various workpiece types, including cabinets, electrical enclosures, and ventilation ducts.
4) High Safety, Low Labor Intensity
Robots replace manual operation in bending heavy metal sheets, avoiding the risks of pinching injuries and misoperation.
The system is equipped with multi-level protection measures such as laser protective gratings, safety fences, and access control interlocks.
Reduces worker labor intensity, improves the working environment, and achieves “human-machine isolation operation.”
5) Stable and Reliable, Reduced Costs
The system has a compact structure, long maintenance cycle, and can operate stably for extended periods.
Automation reduces the number of operators (typically from 2 people to 0-1 people).
Reduces labor costs and scrap rates caused by human error.
The bending machine uses servo energy-saving drives, saving 20%-40% of energy consumption.
6) Intelligent Monitoring and Data Managemen
Rel-time collection of data such as bending angle, pressure, cycle time, and yield.
Integrates with MES/ERP systems for visualized production and traceability management.
Supports remote monitoring and fault diagnosis, improving equipment uptime.
Expandable with AI algorithms for intelligent optimization scheduling and maintenance early warning.
7) Modular Design for Easy Expansion
Flexible combination: single-machine automation, dual-machine collaboration, or full-line integration.
Standardized module interfaces facilitate upgrades and functional expansion.
Supports networking with upstream and downstream equipment (feeders, grinding machines, testing machines).
5. Summary
The robotic sheet metal bending system is an intelligent sheet metal processing equipment that combines industrial robot technology with CNC bending machines. It automates the entire process of sheet metal loading, positioning, bending, flipping, and unloading, achieving automation, intelligence, and unmanned operation of the bending process.
This system has the following key features:
- High Precision: High robot repeatability and consistent bending angles.
- High Efficiency: Continuous automatic operation with stable production cycle.
- High Safety: Avoids manual contact with the bending area with comprehensive protective design.
- Flexible Production: Supports automatic changeover for multiple product types and small batches.
- Intelligent Management: Can connect to MES/ERP systems for data traceability and production visualization.
By applying robotic bending technology, enterprises can significantly reduce labor costs, improve production efficiency, enhance product quality, and accelerate their transformation towards intelligent manufacturing and digital factories.