Table of Contents
Sheet Metal Cone Rolling generally refers to the process of rolling a metal sheet into a tapered cylinder (cone). This is a common shape forming process in sheet metal processing. It is different from ordinary rolling (rolling into a cylindrical shape) because cone rolling involves different diameters at both ends, forming a beveled cone.
1. What is sheet metal cone rolling?
Cone rolling refers to a forming process in which a metal sheet is processed into a conical cylinder (i.e. a cone) through a rolling process. A piece of trapezoidal or fan-shaped sheet is rolled into a cone shaped like a trumpet or funnel by a plate rolling machine. This process is called “cone rolling”.
Definition:
Metal sheet cone rolling is a sheet metal forming process that uses a plate rolling machine to bend the sheet along unequal radii on the basis of adjusting the roller position and pressure to form a conical structure with different diameters at both ends.
Typical characteristics of metal sheet cone rolling:
Features | Description |
Appearance | A tapered cylinder with one end larger than the other |
Sheet shape | Generally a fan-shaped or trapezoidal plate |
Process equipment | Three-roller or four-roller plate rolling machine with adjustable roller position |
Application areas | Ventilation ducts, funnels, chimneys, tapered barrels, mechanical parts, etc. |
2. Key process features of metal plate cone rolling
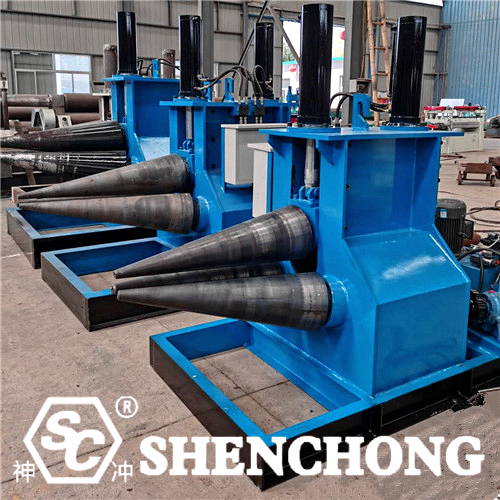

The key process features of sheet metal cone rolling are mainly reflected in the following aspects, which determine its operation mode and difficulty:
1) Special plate shape
Trapezoidal plates or fan-shaped plates are usually used instead of rectangular plates.
When unfolding, accurate unfolding calculation must be performed according to the size of the cone. The unfolding diagram is a section of annular fan.
2) The rolling method is different from ordinary rolling
Ordinary rolling is equal radius rolling (same diameter on both sides).
Conical rolling requires unequal radii on both sides, and one side is tight and the other side is loose during the rolling process to form a taper.
3) The roller needs to be adjusted eccentrically
When rolling the cone, the upper or lower roller needs to be adjusted axially (eccentrically) to generate greater bending force on one side of the plate to form a cone.
Some special plate rolling machines are equipped with taper rolling devices or electric adjustment functions.
4) Forming accuracy depends on experience and adjustment
During the sheet metal cone rolling process, problems such as deviation, slipping, irregular roundness, and loose mouth are prone to occur.
The operator needs to have rich experience and control the rolling trajectory and angle through gradual fine-tuning.
5) The finished product needs post-processing
After rolling, it is usually necessary to carry out processes such as matching, welding, and correction.
Some cones need to be trimmed or shaped to improve the accuracy and appearance.
6) Uneven stress distribution
During the sheet metal cone rolling process, the two sides of the plate are subjected to different forces, which is prone to material rebound, deformation or cracking, especially in thick plates or large taper structures.
7) High requirements for equipment
It is recommended to use a three-roll symmetrical plate rolling machine or a four-roll plate rolling machine with a cone rolling function.
For large-sized or thick plate cones, customized equipment or CNC plate rolling machines may be required.
3. Brief description of the operation steps of metal cone rolling
The operation steps of cone rolling can be briefly divided into the following key links, which are suitable for the processing of conical cylinders using three-roller or four-roller plate rolling machines:
1) Draw the development diagram
According to the parameters such as the large end diameter, small end diameter, height, etc. of the finished cone.
Calculate the generatrix length and development angle.
Get a fan-shaped or trapezoidal unfolded plate shape.
CAD drawing or manual geometry can be used to assist the unfolding design.
2) Material preparation
Cut metal plates (carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, etc.) according to the size of the development diagram.
Deburr the surface of the plate and keep it flat and clean.
3) Pre-bending treatment
Pre-bend both ends of the plate to reduce the straight edge effect of the first and last sections of the rolling.
It can be completed with a plate rolling machine or pre-bending equipment.
4) Plate rolling machine adjustment
Adjust the roller of the plate rolling machine to make one side eccentrically misaligned to form a taper.
Control the misalignment amplitude according to the size of the cone angle.
The taper rolling function can be enabled for equipment with conditions.
5) Start rolling
Send the sheet into the rollers in the set direction and start the machine slowly.
Monitor the rolling process in real time to prevent the sheet from deviating or slipping.
Finely adjust the upper/lower roller position according to the rolling situation.
6) Seam joint
After rolling, adjust both ends to close the seam.
Check the roundness of the cone and the gap between the joints, and perform local shaping.
7) Welding and correction
Spot weld or full weld the seam.
Grind the inner and outer surfaces and correct the roundness if necessary.
For high-precision requirements, mechanical shaping can also be performed.
8) Inspection and subsequent processing
Check the size, roundness, taper, weld quality, etc.
Produce rust prevention, spraying or further assembly as required.
4. How to roll a cone?
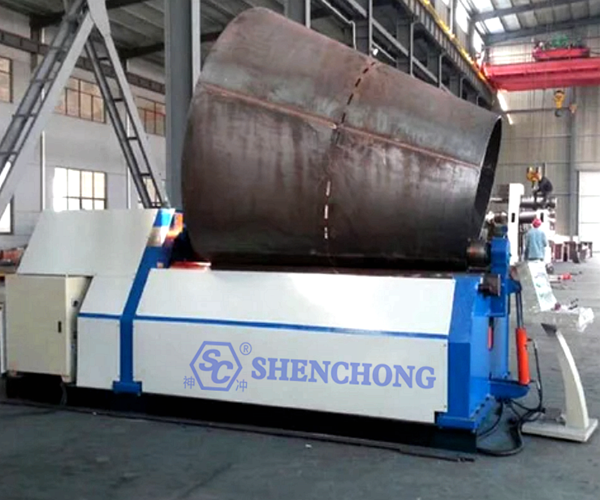

1) Preparation stage
– Clear the size parameters
Large end diameter (D₁)
Small end diameter (D₂)
Cone height (H)
Plate thickness (t)
– Calculate and draw the unfolding diagram
The unfolding diagram is generally a circular sector. The inner and outer arc radii and the unfolding angle are calculated through the geometric relationship of the cone.
CAD or formulas can be used to assist in the calculation.
2) Equipment adjustment
– Select a suitable sheet metal cone rolling machine
If the plate is large and thick, it is recommended to use a three-roller or four-roller plate rolling machine, preferably with a taper rolling function (such as the upper roller can be tilted and adjusted).
If it is just a small conical workpiece, you can buy an affordable special cone rolling machine.
– Adjust the roller misalignment
Offset one side of the upper or lower roller appropriately to form an angle difference.
Tighten one side and relax the other side to achieve a conical rolling effect.
3) Rolling operation steps
– Plate loading
Put the cut sector or trapezoidal plate into the plate rolling machine.
Make sure the large end is on the tight side and the small end is on the loose side.
– Start rolling
Start the equipment slowly and observe the running track of the plate.
Adjust the degree of eccentricity in real time to ensure uniform taper.
Avoid deviation, material jumping, sliding and other problems.
– Rolling in batches (if necessary)
For large tapers or thick plates, two-step method or multiple feeding fine-tuning method can be adopted for segmented rolling.
4) Post-processing
– Seam alignment
After rolling, check the alignment of both sides.
If there is misalignment or out-of-roundness, use a jack, hammer or special rounding machine to adjust.
– Welding and grinding
Spot weld and weld the seams.
Then grind, remove slag and shape to ensure a neat and beautiful surface.
– Inspect the finished product
Check whether the taper, roundness and size meet the standards.
If there is an error, repair or rewind appropriately.
5. Precautions for rolling cones
During the process of rolling cones (i.e. rolling cones), there are several key precautions to ensure the quality of forming, safety and equipment protection:
1) Accurate sheet unfolding
The unfolding diagram calculation must be accurate, especially the angle, radius and generatrix length must not be wrong.
The unfolding diagram is mostly fan-shaped or trapezoidal. Errors will directly lead to rolling failure or difficulty in seaming.
2) Reasonable roller adjustment
When rolling cones, the roller must be eccentrically misaligned, otherwise the taper cannot be rolled out.
The misalignment angle should be adjusted according to the size of the taper. Excessive or small eccentricity will lead to poor rolling.
The plate rolling machine with taper rolling function is more convenient to adjust.
3) Prevent deviation during rolling
Due to uneven force on both sides, the sheet is easy to deviate when rolling cones.
It is necessary to advance slowly during operation, and fine-tune the pressure and position at any time to maintain symmetry.
4) Match the thickness of the sheet with the taper
The thicker the sheet and the larger the taper, the more difficult it is to roll.
For thick plates with large tapers, it is necessary to adjust the segmented rolling several times, and even use hot bending and segmented welding.
5) Pre-bending should be sufficient
Both ends of the plate must be pre-bent to reduce the length of the straight edge at the joint and facilitate the jointing.
Otherwise, problems such as port warping and difficulty in docking will occur.
6) Control of joint accuracy
After rolling, there may be openings and misaligned edges on both sides, which require manual or mechanical assistance for rounding and jointing.
A loose interface will affect subsequent welding and structural strength.
7) Welding should be uniform and timely shaped
Before welding, the positioning should be accurate to avoid shrinkage and deformation.
If there is deformation after welding, cone correction and shaping should be performed.
8) Safety operation specifications
During the rolling process, it is strictly forbidden to touch the roller area with your hands.
Wear protective gloves, goggles, etc. to prevent the plate from bouncing or cutting.
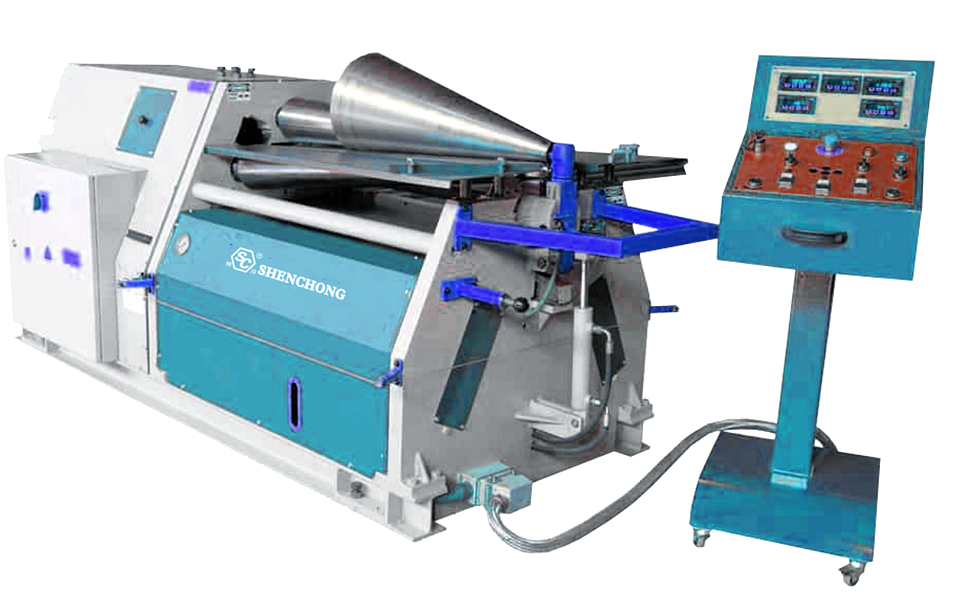

9) Equipment selection should be appropriate
It is recommended to use a three-roller or four-roller plate rolling machine with a taper rolling function.
For extra-thick and extra-large workpieces, consider using a hydraulic heavy-duty plate rolling machine.
10) Finished product inspection cannot be ignored
After forming, key indicators such as taper, roundness, joint clearance, and welding quality need to be checked.
Products with large errors should be corrected or scrapped.
6. Summary and Tips
The process of rolling a metal plate into a cone is to use a plate rolling machine to roll a fan-shaped or trapezoidal plate into a cone cylinder with one end larger than the other. This operation is more complicated than ordinary rolling and requires reasonable equipment adjustment and operation skills.
- Plate thickness: Thick plates are more difficult to roll and require reasonable pre-bending
- Taper size: The larger the taper, the more difficult it is. It is recommended to test a short section first
- Operator experience: The cone rolling operation requires the cooperation of skilled workers, and experience is crucial
- Safety measures: It is strictly forbidden to approach the roller area with your hands and wear protective equipment