Pressure Vessel Industry Background
SC Shenchong can supply complete machine for produce boilers, pressure vessels, heat exchange, storage tank, like 3 rollers plate rolling machine, fiber laser cutting machine, plate shearing machine, CNC plasma cutting machine, heavy duty welding manipulator, welding rotator.
Oil & gas is an industry with companies of the highest level that always look for equipment which can grant the best quality available on the market. The products to be rolled have to be made with the highest accuracy and repeatability is a fundamental requirement to be achieved.
The Main Manufacturing Processes Of Pressure Vessels
The manufacturing process of pressure vessels includes preparation of raw materials, marking, cutting, bending, forming, edge processing, assembly, welding, inspection, etc.
Preparation of Raw Materials
Before marking, the steel needs to be pre-treated. The pre-treatment of steel refers to the purification, straightening, and application of protective primer on materials such as steel plates, pipes, and profiles.
Purification treatment mainly involves removing rust, oxide skin, oil stains, and welding slag from the surface of steel plates, pipes, and sections before marking, cutting, and welding, as well as after cutting, beveling, forming, and welding.
Orthodontics is the process of correcting the deformation of steel during transportation, lifting, or storage.
The main purpose of applying protective paint is to improve the corrosion resistance of steel, prevent oxidation, and extend the service life of components and equipment by applying a layer of protective paint on the surface.
Marking
Marking is the first step in the manufacturing process of pressure vessels, which directly determines the dimensional accuracy and geometric shape accuracy of the formed parts, and has a significant impact on subsequent assembly and welding processes.
Marking is the process of drawing cutting lines, processing lines, various position lines, and inspection lines on raw materials or pre processed blanks, and marking (or writing) necessary signs and symbols. The marking process usually includes the unfolding, layout, and marking of parts. Before marking, the size of the blank should be determined first. The size of the blank is composed of the unfolded dimensions of the parts and various machining allowances. There are several methods to determine the unfolding size of parts:
1) Drawing method: Refers to the use of geometric drawing to unfold parts into flat shapes.
2) Calculation method: Refers to deriving calculation formulas based on the principle of expansion or the principle of unchanged area before and after compression (tension) deformation.
3) Experimental method: Refers to the use of experimental formulas to determine the unfolded dimensions of billets with complex shapes, which is simple and convenient.
4) Comprehensive method: refers to the use of drawing and calculation methods to determine the unfolded size of billets for overly complex parts, and sometimes experimental methods can also be used for verification.
The parts for manufacturing containers can be divided into two categories: expandable parts and non expandable parts, such as circular cylinder and elliptical head, which belong to expandable and non expandable parts respectively.
Cutting
Cutting, refers to the process of separating the required blanks from the raw materials that have been cut through the line. There are two cutting methods: mechanical cutting and thermal cutting.
Mechanical Cutting
Mechanical cutting mainly includes cutting, sawing, milling, and punching, and its characteristic is that mechanical force plays a major role in the cutting process.
Cutting is the process of pressing scissors into a workpiece, causing the shear stress to exceed the material’s shear strength and achieve the goal of cutting. This method has high efficiency and cutting accuracy, and can be used as long as the material hardness and size are appropriate. However, there is obvious hardening phenomenon in the metal 2-3 mm away from the cutting edge. According to the shape of the plane being cut, it can be divided into straight cutting and curved cutting.
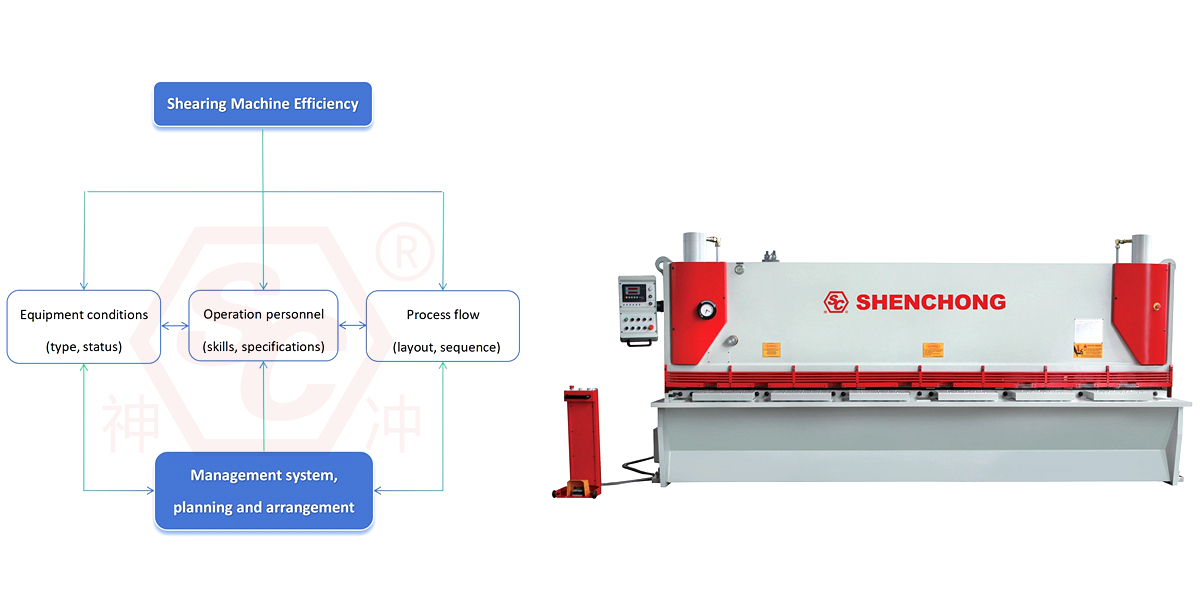
There are two types of shearing machines that use straight long cutting edges for cutting, namely flat mouth shearing machines and oblique mouth shearing machines.
In a flat cut, two straight cutting edges are parallel, and the cutting process is carried out simultaneously along the length of the cutting edge. Therefore, the cutting force is large and the impact is strong, making it suitable for cutting thick and narrow strips.
In oblique cutting, two straight cutting edges intersect at a certain angle, and the cutting process gradually proceeds along the length of the cutting edge. Therefore, the cutting force is smaller than that of a flat cutting when cutting workpieces of the same thickness, reducing the impact and making it suitable for cutting thin and wide sheet metal.
In equipment manufacturing, gantry shearing machines are often used to cut straight workpieces. This shearing machine is convenient to use, has simple feeding, fast cutting speed, and high accuracy. To produce small storage tank that the plate thickness is not very thick, clients also can choose plate shearing machine to cut the plate.
Oxygen Cutting
Oxygen cutting is abbreviated as gas cutting, also known as flame cutting. Oxygen cutting belongs to thermal cutting, which requires a preheating flame during cutting. However, flame alone cannot achieve cutting, and the key is to have a high-speed pure oxygen airflow.
Plasma Cutting
Plasma is a state of matter in which all substances are ionized into positive and negative ions. Plasma cutting is the use of high-temperature and high-speed plasma flames to fuse materials and form notches, which belongs to the high-temperature melting and cutting in thermal cutting. It is not limited by physical properties and can cut both metal and non-metal materials, but is mainly used for cutting stainless steel, aluminum, copper, nickel, and their alloys.
Laser Cutting
With the development of fiber laser cutting technology, the cutting capacity of fiber laser cutting machine dramatically increase and the price decrease a lot. Currently, more and more clients choose to buy fiber laser cutting machine to replace the plasma cutting machine.
Bending
Bending And Rolling of Cylinder Body
The cylinder body is composed of several cylinder sections welded through circumferential welds, and the cylinder sections are welded through plate rolling and longitudinal welds. The rolling principle of this cylinder section is also known as rolling plate, which is the basic manufacturing method of the cylinder section. The rolling bending principle is to use a plate rolling machine to apply continuous and uniform plastic bending to a steel plate to obtain a cylindrical surface.
Bending Of Head
There are three main methods for forming the head: stamping, spinning, and explosive forming. The currently commonly used methods are stamping and spinning.
Welding
Welding is a process that involves heating, applying pressure, or a combination of both to achieve atomic bonding and form a permanent joint. Welding processes participate in 50% of the world’s annual steel consumption.
Welding can be divided into three categories: fusion welding, pressure welding, and brazing.
Fusion Welding
The processing method of locally heating the workpiece to be welded until it melts, condensing it to form a weld and connecting the components together. Including arc welding, gas welding, electric slag welding, electron beam welding, laser welding, etc. Fusion welding is a widely used welding method, and most low-carbon steel and alloy steel are welded using fusion welding. Special fusion welding can also weld non-metallic materials such as ceramics and glass.
Pressure Welding
Pressure must be applied during the welding process, which may or may not be heated to complete the welding. The main purpose of its heating is to soften the metal, by applying pressure to plastic the metal and bringing atoms closer to a distance of stable attraction to each other, which is fundamentally different from heating during fusion welding. Pressure welding includes resistance welding, friction welding, ultrasonic welding, cold pressure welding, explosive welding, diffusion welding, and magnetic welding. Its characteristics include small welding deformation, few cracks, and easy automation.
Brazing
The welding method involves heating the brazing material with a lower melting point than the base metal until it melts, but the heating temperature is lower than the melting point of the base metal. The melted brazing material is used to fill the weld seam, wet the base metal, and diffuse with the base metal to form a whole. Brazing can be divided into two categories: hard brazing and soft brazing. The heating temperature of brazing is greater than 450 ℃, and the tensile strength is greater than 200MPa. Silver and copper based brazing materials are often used, which are suitable for situations with high working stress and high environmental temperatures, such as the welding of hard alloy turning tools and geological drill bits. The heating temperature of soft soldering is less than 450 ℃, the tensile strength is less than 70MPa, and it is suitable for environments with low stress and low working temperature, such as tin based soldering of circuits.